What is a cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
Is it the same as heart disease? Read on to find out that and more…
September 29 is universally acknowledged as World Heart Day. A World Heart Federation (WHF) initiative, this Day is observed to increase awareness of heart disease and advocate for worldwide prevention, control, and reduction in such diseases. The theme chosen for this year’s World Heart Day is “My Heart, Your Heart.”
“It’s about saying to ourselves, the people we care about and individuals all around the world, ‘what can I do right now to look after MY HEART… and YOUR HEART?‘ It also resonates with the professional cardiology and healthcare audiences who dedicate themselves to looking after ALL OUR HEARTS,” cites the WHF campaign.
Undoubtedly, a noble theme for a noble cause and so important in the current times when our dependency on fast-food joints has reached its zenith courtesy our fast-paced lives. Our professional lives have literally left no time for us to work on our lifestyle, at least for the better. The hurried, takeaway coffee and donut mornings, two-minute luncheons and not to forget the caffeine and smoking addiction have sent the trajectory of our health on a downward spiral.
Indians and Cardiovascular diseases
A new study published in the American College of Cardiology paints a grim picture of India’s heart problem. It states that between 1990 and 2016 the death rate due to CVD in India increased by 34 percent- from 155.7 to 209.1 deaths per one lakh population.
The authors of the study feel that the consumption of tobacco and lifestyle choices aiding in high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels are key factors of the rise in CVD death rate. The study said that India needs to strengthen its national, regional and local health systems to fight this alarming trend.
In addition to this, another study published in The Lancet Global Health stated that one-fourth of all deaths that occurred in India in 2015 were due to CVD. The Global Burden of Disease study funded by Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation in cooperation with the World Health Organization said the death rate due to CVD in India of 272 per 100000 population is higher than the global average of 235 per 100000 population.
If we go by these calculations then CVD and heart diseases are the leading cause of deaths in India.
Cardiovascular disease or Heart Disease?
CVD is an umbrella term for all types of heart and blood vessels-related diseases. These include coronary heart disease (clogged arteries), which may cause heart attacks, congenital heart defects, stroke, and congenital heart failure. Let us find out what these are.
Heart Disease
This term has become a catchphrase for many conditions that adversely affect the functions and structure of the heart. While all heart diseases are CVDs, all CVDs may not be heart diseases. However, coronary heart disease is one of the most common heart afflictions.
Coronary heart disease
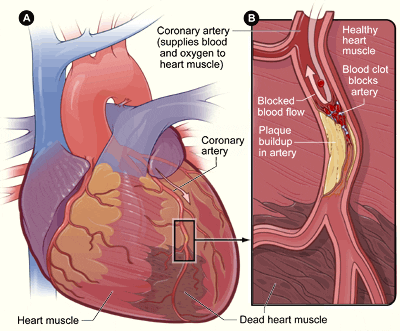
This is a condition when fat, calcium and cholesterol including other substances combine to form plaque. This plaque gets deposited in the arteries which then become clogged. Such a condition is called atherosclerosis which stops blood enriched with oxygen from reaching the heart. This can cause chest pain or angina. Furthermore, if allowed to accumulate, plaque can cause blood clots which may block the flow of blood, causing a heart attack.
Myocardial infarction
Also called heart attack, coronary thrombosis and cardiac infarction, this condition is caused when a part of the heart muscle is damaged. An irregular supply of blood due to a blood clot may cause such damage. It can also happen when an artery spasms or narrows suddenly.
Stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot appears in the vessel that supplies blood to the brain. Such a blockage can make the brain lose control over body functions like talking and walking.
Hemorrhagic stroke is when, due to hypertension or high blood pressure, a blood vessel in the brain bursts. Brain cells are irreplaceable and thus, sometimes, the consequences of a stroke may be permanent. However, at times, the brain cells incur only some damage which gets repaired over time. Rehabilitation occurs gradually and improves speech and other body functions.
Heart failure
Also known as congestive heart failure it happens when the heart does not pump blood the way it should. Heart failure doesn’t mean that the heart has stopped, rather it keeps working but the body’s requirement for oxygen and blood is not being met. It should be treated immediately because if untreated, it can turn fatal.
Arrhythmia
An abnormal heartbeat is Arrhythmia. The heart rhythm could be too slow (Bradycardia, less than 60 beats a minute), too fast (Tachycardia, 100 beats or more a minute) or irregular. Arrhythmia can adversely affect the body as an irregular heartbeat may not pump the required blood for the body’s need.
Problems with the heart valve
Stenosis occurs when valves of the heart do not open properly to allow the flow of blood. Regurgitation, as the name suggests, happens when the blood leaks through when the valves do not close properly. Prolapse occurs when the valve bulges upwards or back in the heart’s upper chamber.
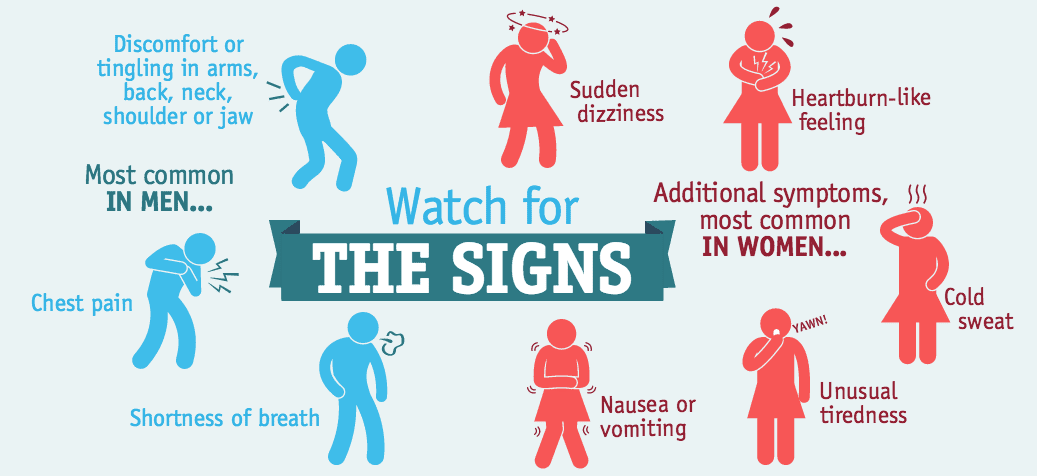
The Symptoms
Common symptoms of heart diseases, among others, are breathlessness, palpitations, chest pain (called angina which can occur in case of lack of blood supply to the heart). Physical exertion and stressful events may trigger angina too and may return to normal, under 10 minutes. Sometimes heart attack symptoms mimic the symptoms of indigestion. A stomach ache and heartburn may also occur along with a heaviness in the chest.
Other symptoms may include:
- Pain traveling from the chest to the arms, neck, jaw, abdomen or back
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Sweating profusely
- Vomiting or feeling nauseous
The Causes
Apart from genetic heart disease like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or congenital heart problems, lifestyle choices can have a major impact on heart health.
Lifestyle choices harming your heart include:
- Neglecting high blood pressure and cholesterol
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- A family history of heart ailments
- Disregarding diabetes
- Eating too much junk food
- Prolonged periods of inactivity
Treatment
Medications and surgery are two treatments for heart disease. Some of the surgical treatments include:
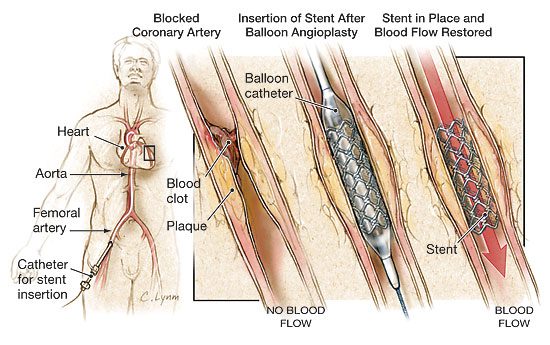
- Angioplasty: Insertions of a balloon catheter to widen the blood vessels for smooth blood flow.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is done on people whose arteries are blocked. This allows the flow of blood to reach blocked parts of the heart.
- Repairing or replacement of damaged heart valves
- Pacemakers, or machines to regulate heartbeats for patients with arrhythmia
Heart transplant could certainly be another option if a heart of the correct size and blood type is acquired in time.
Prevention
Congenital or genetic heart disease cannot be prevented. However, some measures can be taken to avoid other types of heart diseases:
- Consuming a balanced diet: Low-fat, high-fiber foods, fresh fruit, and vegetables are a go-to for a healthier heart. Use unsaturated oils in your diet and eat whole grains. Reduce the intake of caffeine, salt, sugar, and processed foods.
- A daily regime of exercise: This helps in maintaining blood pressure, cholesterol levels and strengthens your heart.
- Go cold turkey on smoking: Smoking is injurious to health, the packet says it all.
- Reducing alcohol consumption: can help your heart in the long run.
These measures do not eliminate the risk of developing a heart complication. They certainly improve your overall health and minimize the chances of heart disease. Ideally, follow the healthy tips offered here, help others with the same, and you will be able to say, “I look after my heart… and your heart!!”